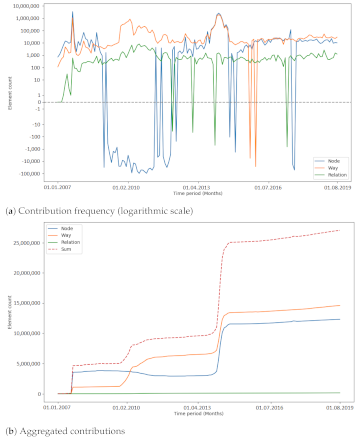
OpenStreetMap (OSM) is a global mapping project which generates free geographical information through a community of volunteers. OSM is used in a variety of applications and for research purposes. However, it is also possible to import external data sets to OpenStreetMap. The opinions about these data imports are divergent among researchers and contributors, and the subject is constantly discussed. The question of whether importing data, especially large quantities, is adding value to OSM or compromising the progress of the project needs to be investigated more deeply. For a recent study by Witt et al. published Open Access, OSM’s historical data were used to compute metrics about the developments of the contributors and OSM data during large data imports which were for the Netherlands and India. Additionally, one time period per study area during which there was no large data import was investigated to compare results. For making statements about the impacts of large data imports in OSM, the metrics were analysed using different techniques (cross-correlation and changepoint detection). It was found that the contributor activity increased during large data imports. Additionally, contributors who were already active before a large import were more likely to contribute to OSM after said import than contributors who made their first contributions during the large data import. The results show the difficulty of interpreting a heterogeneous data source, such as OSM, and the complexity of the project. Limitations and challenges which were encountered are explained, and future directions for continuing in this field of research are given.
Regarding the contribution patterns and the development of tag keys, no specific impact of large data imports was found in this study. The number of unique tag keys increased as the number of elements increased, given that external information was mapped to OSM tags. More research is needed to understand how the community is changing OSM data after a large data import.
The study considered the impact of large data imports from a data perspective on a small subset of imports that were conducted. For future research, the analysis of different data imports might also incorporate other aspects of OSM—for example, community events or mapping events and how they are related to imports. The investigation of automated processes, e.g., scripts or bots, could lead to better understanding about how large chunks of imported data are changed. Moreover, the phase of OSM in which an import is conducted could be analysed more thoroughly. This might help to understand if an import could be performed to also support the establishment or growth of a community in a specific region. Additionally, in that regard, the effect of the media or the OSM community creating awareness about data donations and respective data imports needs to be investigated. Additionally, the analysis of OSM contributors could be extended, for example, by considering the locations of contributors who are involved in an import process. Emerging spatial patterns could help to understand how local communities are developing during an import. The attributes of imported elements and how they are evolving over time could be analysed with a focus on the semantics of the data.
Witt, R.; Loos, L.; Zipf, A. (2021): Analysing the Impact of Large Data Imports in OpenStreetMap. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10080528

Selected earlier & related work:
- Raifer, Martin; Troilo, Rafael; Kowatsch, Fabian; Auer, Michael; Loos, Lukas; Marx, Sabrina; Przybill, Katharina; Fendrich, Sascha; Mocnik, Franz-Benjamin; Zipf, Alexander (2019): OSHDB: a framework for spatio-temporal analysis of OpenStreetMap history data. Open Geospatial Data, Software and Standards.
- Herfort, B., Lautenbach, S., Porto de Albuquerque, J., Anderson, J., Zipf, A. (2021): The evolution of humanitarian mapping within the OpenStreetMap community. Scientific Reports 11, 3037 (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-82404-z
- Fritz, O., Auer, M., Zipf, A. (2021). Entwicklung eines Regressionsmodells für die Vollständigkeitsanalyse des globalen OpenStreetMap-Datenbestands an Nahverkehrs-Busstrecken. AGIT ‒ Journal Für Angewandte Geoinformatik. 7-2021
- Roick, O., Hagenauer, J., & Zipf, A. (2011). OSMatrix—Grid based analysis and visualization of OpenStreetMap. State of the Map EU, Wien.
- Jokar Arsanjani, J., Mooney, P., Helbich, M., Zipf, A., (2015): An exploration of future patterns of the contributions to OpenStreetMap and development of a Contribution Index, Transactions in GIS, 19(6): 896–914. John Wiley & Sons. DOI: 10.1111/tgis.12139.
- Grinberger, A.Y., Schott, M., Raifer, M., Zipf, A. (2021): An analysis of the spatial and temporal distribution of large‐scale data production events in OpenStreetMap. Transactions in GIS. 2021; 00: 1– 20. https://doi.org/10.1111/tgis.12746
- Schott, M., Grinberger, A.Y., Lautenbach, S., Zipf, A. (2021): The Impact of Community Happenings in OpenStreetMap — Establishing a Framework for Online Community Member Activity Analyses. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10030164
- Auer, M.; Eckle, M.; Fendrich, S.; Griesbaum, L.; Kowatsch, F.; Marx, S.; Raifer, M.; Schott, M.; Troilo, R.; Zipf, A. (2018): Towards Using the Potential of OpenStreetMap History for Disaster Activation Monitoring. ISCRAM 2018. Rochester. NY. US.
- Barron, C., Neis, P. & Zipf, A. (2013): A Comprehensive Framework for Intrinsic OpenStreetMap Quality Analysis. , Transactions in GIS, DOI: 10.1111/tgis.12073.
- Ludwig, C.; Fendrich, S.; Zipf, A. (2020): Regional variations of context‐based association rules in OpenStreetMap. Transactions in GIS. Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1111/tgis.12694
- Ballatore, A. and Zipf, A. (2015): A Conceptual Quality Framework for Volunteered Geographic Information. COSIT – CONFERENCE ON SPATIAL INFORMATION THEORY XII. 2015. Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 1-20.
- Yang, A., H. Fan, N. Jing, Y. Sun, A. Zipf (2016): Temporal Analysis on Contribution Inequality in OpenStreetMap: A Comparative Study for Four Countries. ISPRS Int. Journal of Geo-Information. 5(1), 5.
- Li, H., Herfort, B., Zipf, A. (2019): Estimating OpenStreetMap Missing Built-up Areas using Pre-trained Deep Neural Networks. 22nd AGILE Conf. on Geographic Information Science, Limassol, Cyprus.
- Wu, Zhaoyan, Li, Hao, & Zipf, Alexander. (2020). From Historical OpenStreetMap data to customized training samples for geospatial machine learning. In proceedings of the Academic Track at the State of the Map 2020 Online Conference, July 4-5 2020. DOI: http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3923040